
Director of Operations | Fall'20
Creating, Organizing, and Managing a team for your online business can be fairly daunting, however with the proper understanding of the stakeholders involved and the various roles they play is critical to the success of your business or non-profit venture. There are 3 main roles in any product team: designer, developer, and product manager.
A designer makes sure that a product looks visually appealing, and more importantly that the user experience is smooth and frictionless. A developer handles many of the technical hurdles that come with creating a digital product from making sure your product communicates with the proper hosting services to ensuring a functional experience for the end user. Product managers help lead this cross functional team by conducting research on users, setting a roadmap, and defining features for a product or product line.

"Design is intelligence made visible."
Design is a discipline that originated from limitation. It has been present in human culture since ancient times and resulted in many of the geometric feats of architecture and space such as the Pyramids and the Duomo in italy.
In modern technology design the focus has expanded to include the experience of the end user as well. Not only must products be visually appealing but, they must be organized and flow in such a way that is functionally optimal. Any of the graphics, animation, or general movement of an application or website was most likely created by a designer.
If you want to know more about the history of UI/UX design here is a great video you should check out:

To get started in design check out our design curriculum, or if you just want to learn more about the basic principles check out HackDesign linked above.
"Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic." - Arthur C. Clarke
This quote was the third law of technology that science fiction author Arthur C. Clarke layed out in his essay "Hazards of Prophecy: The Failure of Imagination". With the first two being:
- When a distinguished but elderly scientist states that something is possible, he is almost certainly right. When he states that something is impossible, he is very probably wrong.
- The only way of discovering the limits of the possible is to venture a little way past them into the impossible.
Like magicians engineers often must work on the bounds of what humans think is possible. From the users perspective their work many times seems nonexistent, effortlessness working in the background powering the services they use. Developers are in charge of building the foundation of the product or service you are building, and without them designers wouldn’t be able to build beautiful interfaces on top of the product. Think of developers as the internal organs of any project, invisible to the viewer, but ultimately what allows the project to survive and function.
To explain what a software engineer does would be a tedious project and something that warrants far more that just a page of information, however, Jarvis Johnson does an excellent job explaining his degree succinctly in this video:
Project managers help organize projects and guide teams towards defined goals. They should be familiar with the capabilities, duties, and tools of designers & developers even if they don’t have a mastery over them. They help make strategic product decisions that deliver value to users based on their research.
Being a product manager means not only understanding how the product will function in peoples hands, but making sure that all of a users needs are met. To do this they must define the why, when, and what of the product that the engineering and design team builds. Ultimately a product manager's duties can be summarized through four processes: strategy, releases, ideation, and features.
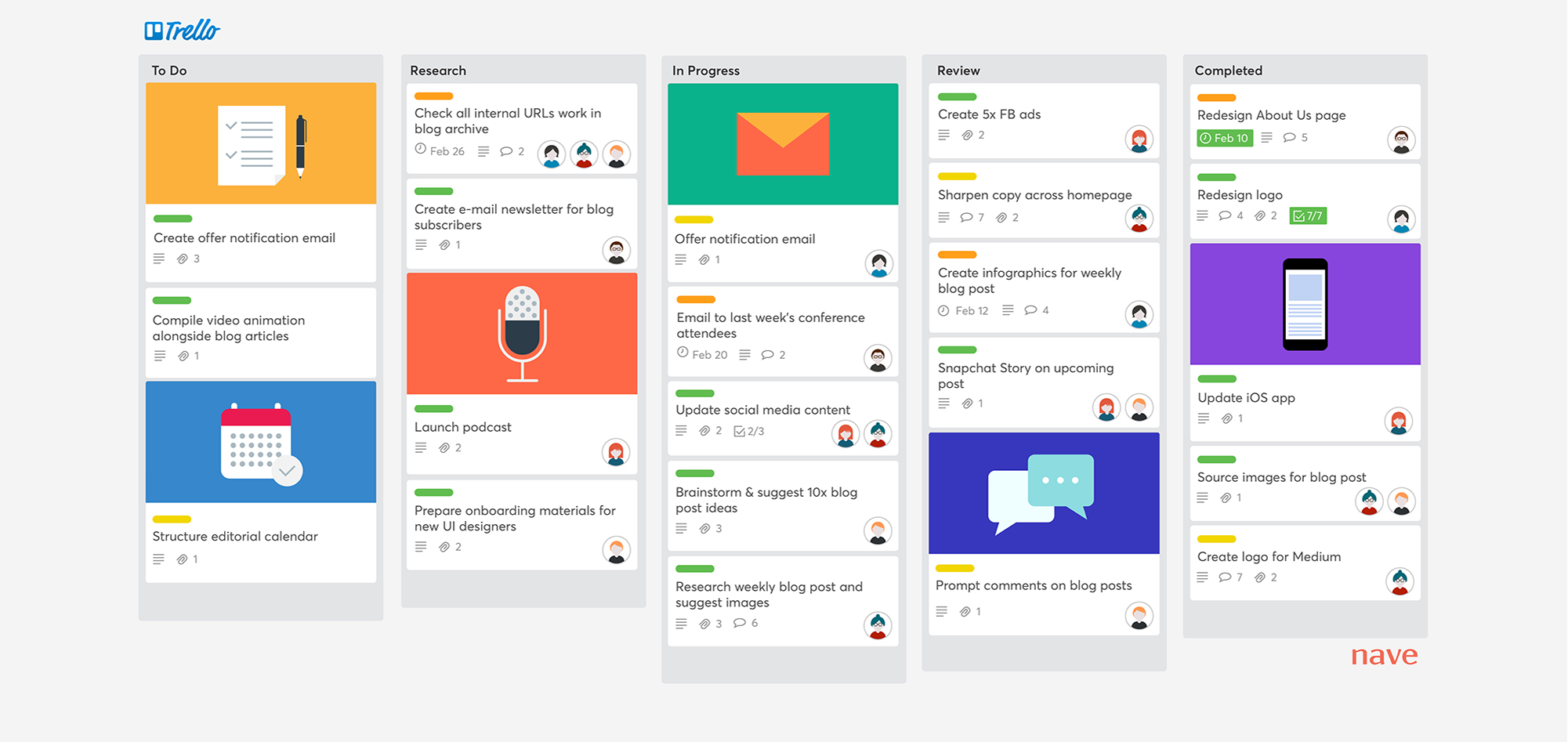
Strategy
This job requires a product manager to clearly articulate the business value of the project to the team. They must prioritize building what's most important first and sort through the tradeoffs of various features. Many times PMs will use management tools such as Trello, Asana, or Notion.
Releases
PM’s must plan a delivery timeline for their projects features. This means having a deep understanding of your project and your team's capabilities. Establishing a timeline that is not only expedient but comfortable for your team is critical to one’s success as a product manager.
PM’s must also bridge the gaps between the company to make sure the release of the product is harmonious. This means reaching out and working with the marketing team, sales team, and customer support to ensure all parties are on the same page for launch.
Ideation
Fresh ideas are the hallmark and lifeblood of any company or organisation. It is the product manager’s role to curate and develop new ideas collaboratively with their teams. Oftentimes this means just listening to people who have more experience or are experts in a separate field. PM’s must determine not only what ideas are good, but which ones will push the product strategy forward in parallel with the interests of the business they are working in. To do this they must constantly integrate feedback from users, developers, and designers back into the product to create its best possible version.
Features

A product manager must not only figure out the plethora of features that could be added to the product, but organize and prioritize them in such a way to preserve the strategic interests of the product's function. This means laying out the requirements of the most important features and visualizing what the desired user experience looks like.
For more information on product management check out our recent Fireside chat speaker Julie Zhuo's book, The Making of a Manager:


Sequoia Capital, one of the largest Venture Capital firms in the world has a pitch deck template they suggest companies looking for investment use. It offers a great framework for not only assembling your pitch deck, but also for organizing your business idea into actionable steps.
Finding your company purpose is an exercise in concisely articulating the heart of your company. This should be formulated in one powerful declarative sentence.
The problem you are addressing should be a pain that currently exists for your target consumer. Make sure to think about how consumers currently address this problem.
Your solution is how you improve your customers life through solving the pain point you discussed previously. This is where you show where your product fits and what its use cases are.
The next question you should ask yourself is “Why Now?”. To answer this question, you must evaluate your problem historically and why solutions have failed for it. This means finding data and trends in the modern world that support your hypothesis of launching the product.
Finding your market means identifying the customer that you are trying to win over. The more specific you are, the more likely you will be able to address that demographic’s unmet needs.
Do research on your competitors. See what features their products have, and how they attempt to solve your problem. List out reasons why your product would be better and why it wouldn’t. Competitors are not a bad thing when it comes to starting a business. It means that your hypothesis of the market problem is correct because there are other organizations looking to solve it as well.
Once you have taken the time to think about your idea conceptually it is time to build it out. Create and showcase your product or prototype. Make sure to highlight its function, utility, and user scenarios.
Finally, once you’ve built a product that solves the problem and have found a product market fit, you can begin thinking about how to monetize your product (if you haven't already). This means establishing pricing for your product, a revenue model, finding lifetime value of customers, and creating a pipeline to distribute and sell your product.
Make sure to credit your team for the amazing work they put in, because ultimately they are the most important and valuable part of any business venture.

.png)